Inflation is an economic phenomenon that directly impacts citizens’ purchasing power and market stability. Over the past decade, the European Union has experienced significant changes in consumer prices, shifting from near-zero inflation rates to record highs due to various economic and health crises.
A Decade of Inflationary Changes
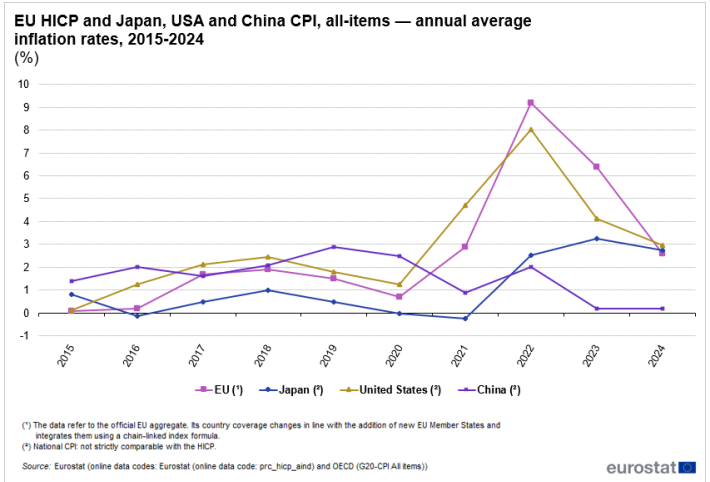
In 2015, inflation in the EU was at a low of 0.1%, reflecting a period of stability following the global financial crisis. However, in the following years, inflation gradually increased: 0.2% in 2016, 1.7% in 2017, and 1.9% in 2018. In 2019, it slightly declined to 1.5%, and in 2020, due to the COVID-19 pandemic, inflation dropped significantly to 0.7% as a result of reduced demand and lockdown measures.
The situation changed drastically in 2021 when inflation rose to 2.9%, driven by economic recovery and supply chain disruptions. In 2022, the energy crisis and geopolitical tensions caused a record surge to 9.2%, the highest inflation rate recorded in the EU’s recent history. In 2023, inflation declined to 6.4%, still above the 2021 level, and in 2024, it stabilized at 2.6%.
Between 2015 and 2024, the EU’s Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices (HICP) accumulated a total variation of 30.2%, with an average annual rate of 3.0%.
Global Comparison: How Did Other Economies Perform?
When looking at price trends globally, significant differences emerge between regions. While the EU recorded an average annual inflation rate of 3.0%, Japan experienced a much lower rate of 1.1%. In contrast, the United States had a slightly higher inflation rate than the EU, at 3.2%, while China maintained a rate of 1.6%.
Within the EU, the countries with the highest HICP increases between 2015 and 2024 were Hungary (66.6%), Estonia (55.1%), and the Czech Republic (51.9%). On the other end, Cyprus had the lowest inflation increase at 17.1%.
Inflation in 2024: Which Countries and Sectors Were Most Affected?
In 2024, Romania had the highest annual inflation rate in the EU, with consumer prices rising by 5.8%. Belgium (4.3%) and Croatia (4.0%) also recorded high inflation rates. In contrast, Lithuania (0.9%), Finland (1.0%), and Italy (1.1%) had the lowest inflation levels.
By sector, alcoholic beverages and tobacco saw the highest price increase in 2024 (5.6%), followed by restaurants and hotels (5.2%) and education (4.9%). Communications was the only sector that experienced a price decrease, dropping by 1.4%.
Over the past decade, food and non-alcoholic beverages saw the highest cumulative increase in the EU (42.8%), followed by alcoholic beverages and tobacco (41.6%). Meanwhile, communication prices declined by 4.3% over the same period.
source: EUROSTAT